A Comprehensive Guide to Building a Robust Data Portal using CKAN
Luccas Mateus
The PortalJS CKAN example intends to provide users with an easy way to bootstrap a data catalog and share data stories backed by a CKAN back end. The configuration is simple, being a matter of simply setting up an environment variable, which determines from which CKAN instance the data is going to be pulled.
Demo
To get a feel of the project, check out the demo at live deployment.
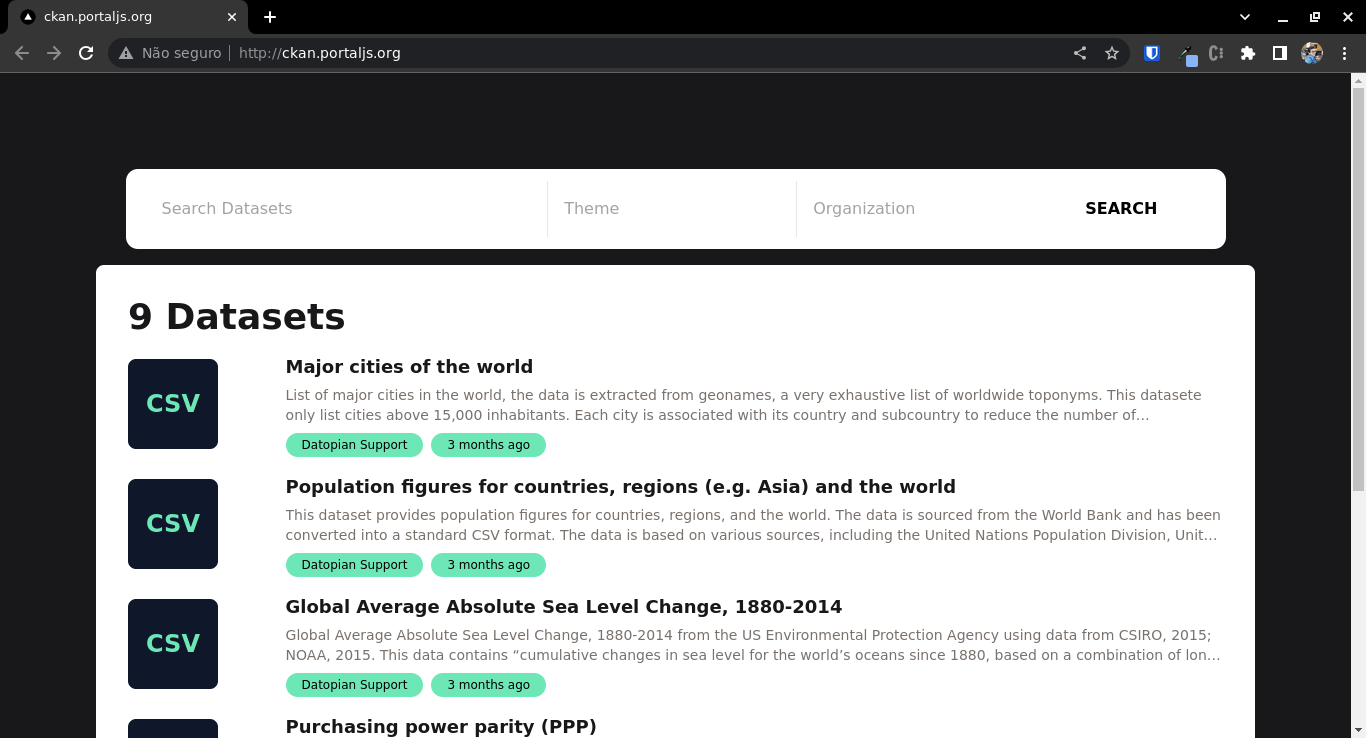
Front page
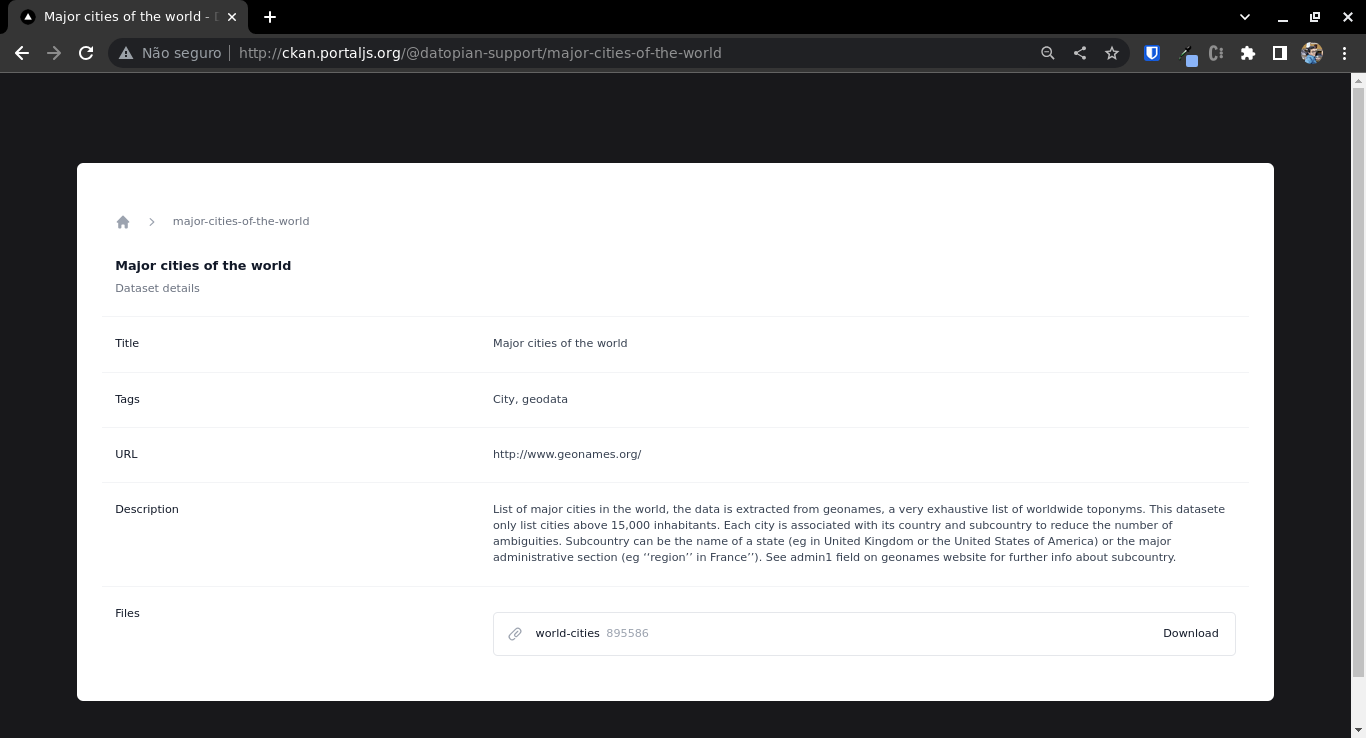
Individual dataset page
How to use this example as a template
Create a new app with create-next-app:
Navigate to the directory in which you want to create the project folder and run the following command:
npx create-next-app <app-name> --example https://github.com/datopian/datahub/tree/main/examples/ckan
cd <app-name>
Point to the CKAN instance
This project uses CKAN as a backend, so you need to point it to the desired CKAN instance URL. You can do so by setting up the DMS environment variable in your terminal or creating an .env file with the following content:
DMS=<ckan url>
Run the app
To run the app in development mode, execute the following command on a terminal:
npm run dev
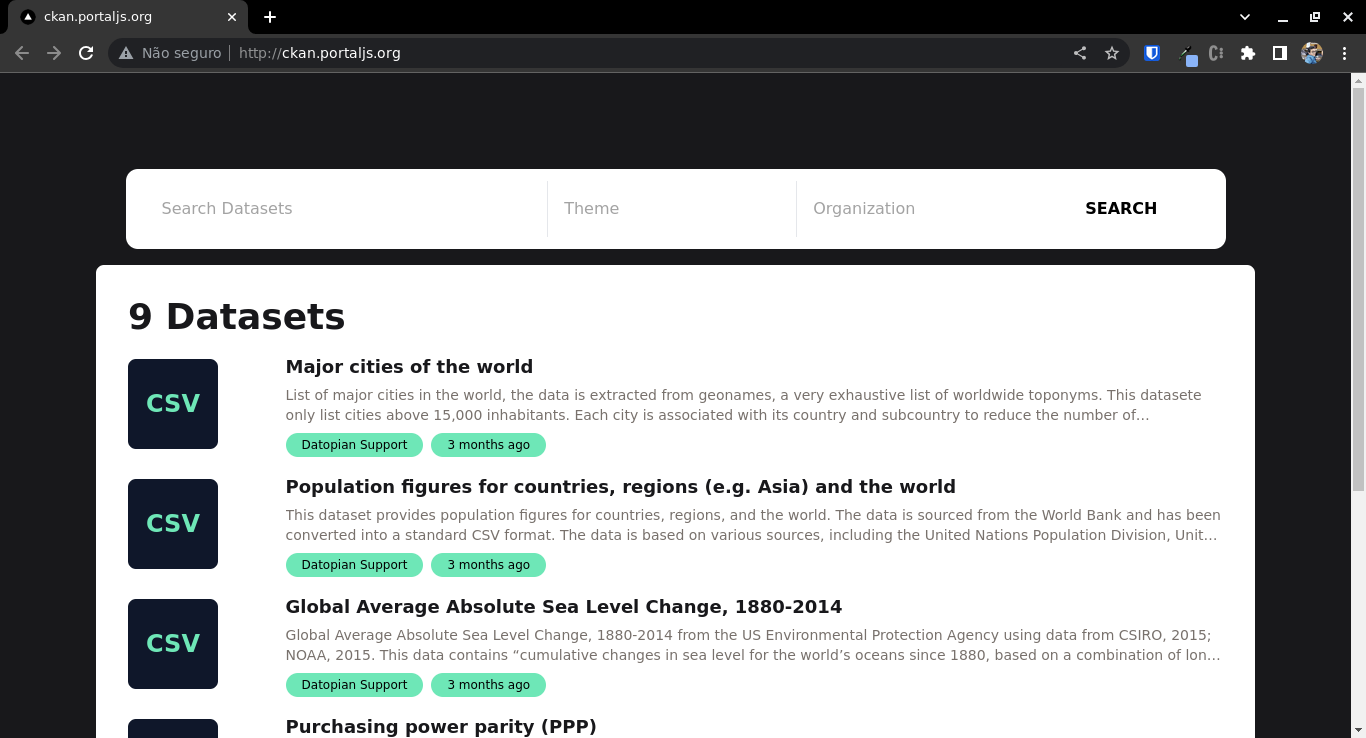
Congratulations, you now have something similar to this running on http://localhost:3000:
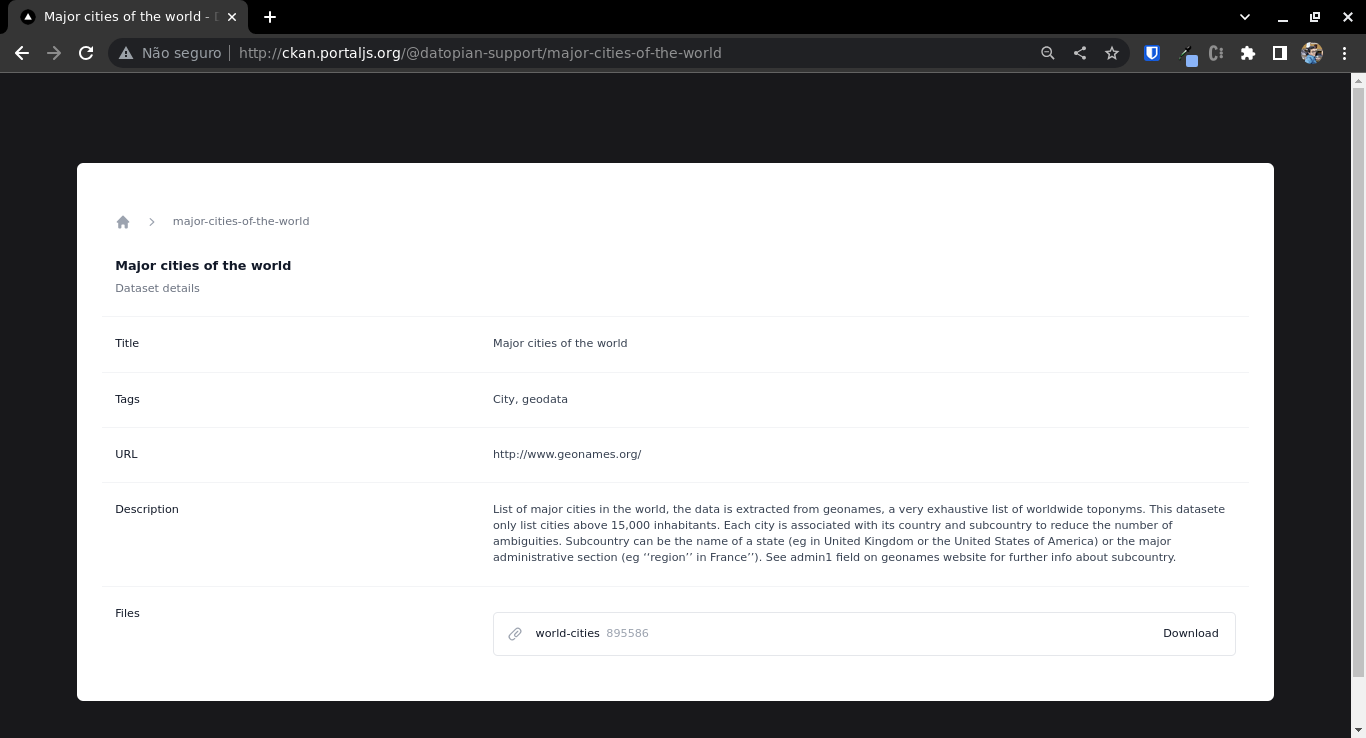
If you navigate to any of the dataset pages by clicking on the dataset title you will see something similar to this:
Deployment
By clicking on this button, you will be redirected to a page which allows you to clone the base project into your own GitHub/GitLab/BitBucket account and automatically deploy it.
Extra commands
You can also build the project for production with
npm run build
And run using the production build like so:
npm run start
CORS Issues
The template has a built-in CORS proxy, in case you have any CORS issues when fetching files. All you need to do is route your HTTP request through the proxy.
Basically instead of calling given URL you will call /api/cors?url={your url}, and the CORS issue shall be gone.
Data-Rich Documents
In this example there is a content folder. Markdown files in this folder are going to be rendered as pages in the application.
Those, however, are not ordinary Markdown pages: they are what we call Data Rich Documents. This means that besides common Markdown, those pages are also capable of rendering data components. This capability allows for the creation of data stories.
The way it works is that these documents support the MDX syntax, which allows React components in Markdown files, in the case of this example, making all the components in the PortalJS components library available on Markdown pages.
So, for example, you can add the following content to the /content/test.md file:
# VIX Daily Report
<FlatUiTable url="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datasets/finance-vix/main/data/vix-daily.csv" />
And from your browser go to /stories/test. You will see the following:
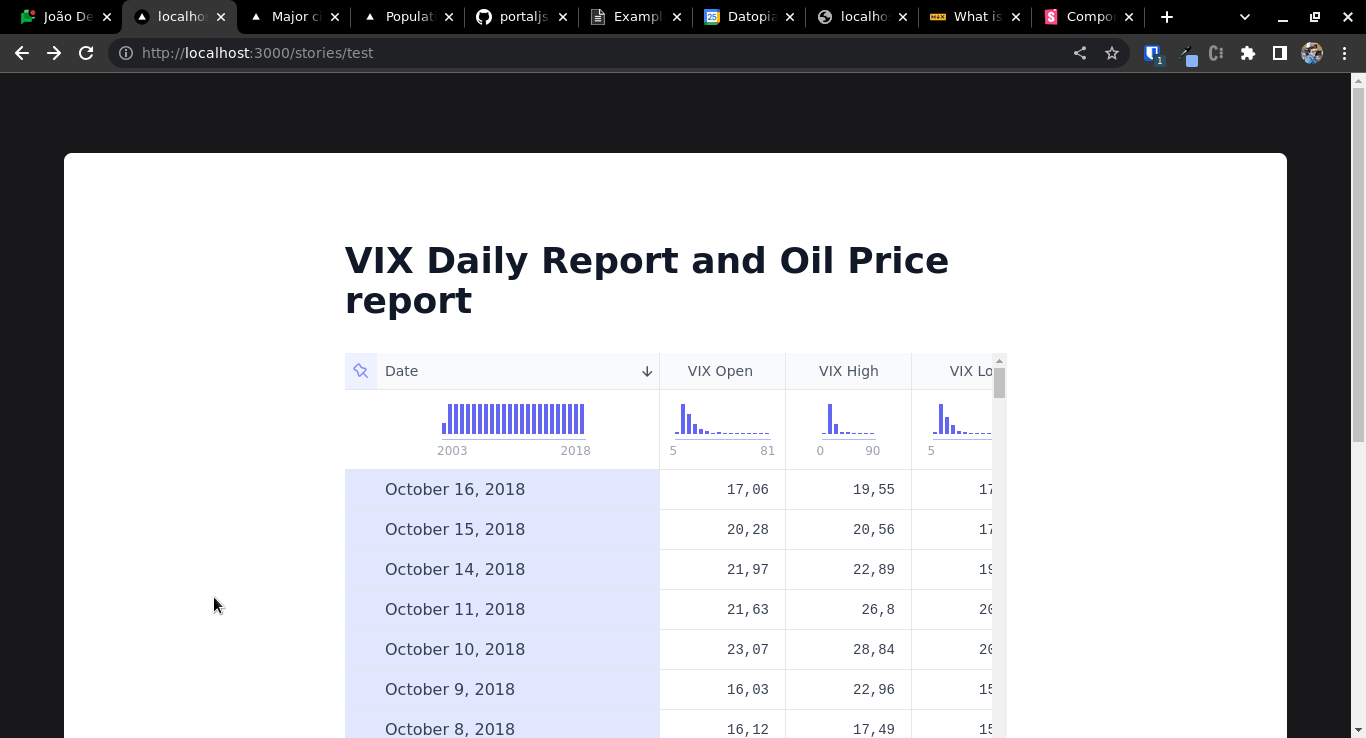
In this file you also have access to the available datasets metadata by simply editing the file's frontmatter e.g. replace the content of /content/test.md with this:
---
datasets: ['population-figures-for-countries-regions-e-g-asia-and-the-world', 'major-cities-of-the-world']
---
# My datasets
## Names
<span>{datasets.map(dataset => dataset.title).join(', ')}</span>
Now run npm run mddb (always run this command after updating frontmatter, this example is using MarkdownDB to index the Markdown files and this command tells MarkdownDB to reindex the metadata) and you should see something like this:
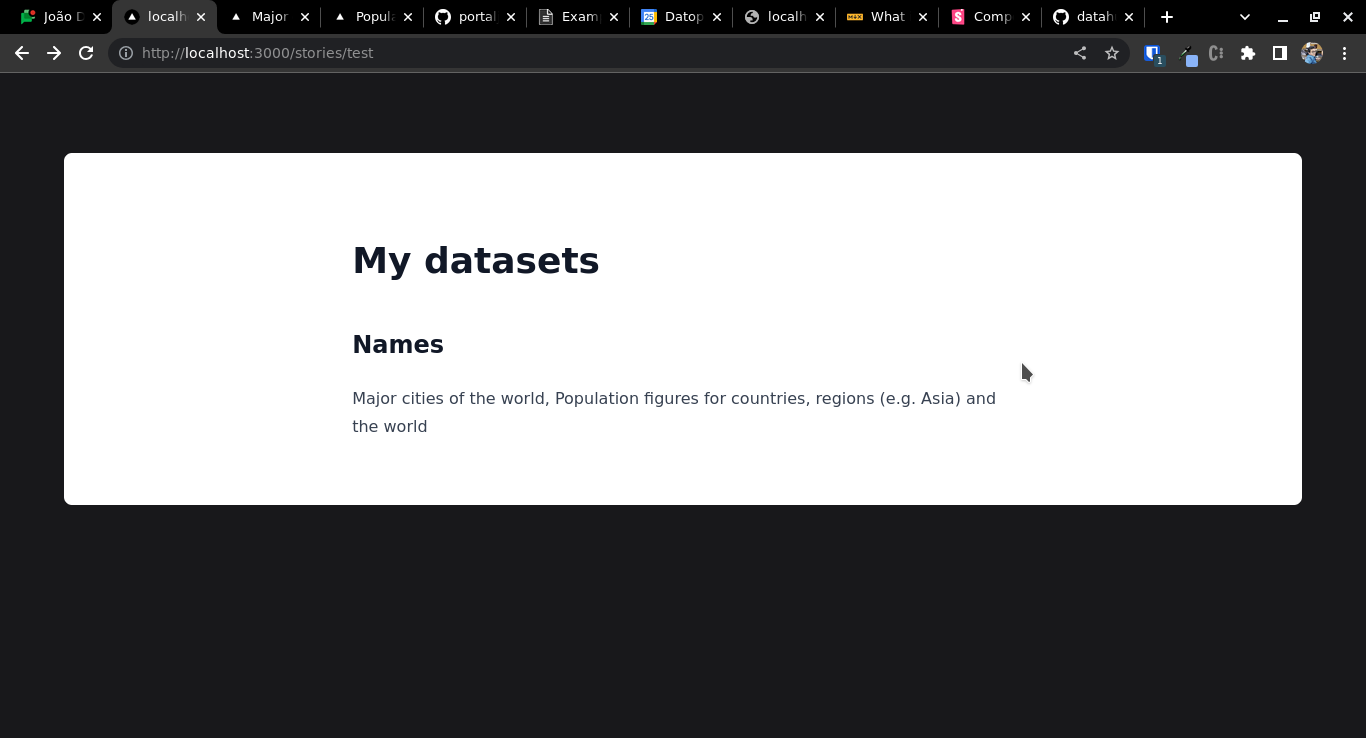
Note that what's happening here is that the "datasets" variable becabe available in the Markdown file, containing the metadata of the datasets whose name was passed to the Frontmatter section.
Extra steps
Feel free to customize your portal, a few suggestions would be.
- Connecting to a different CKAN backend and seeing how it looks
- Using the CKAN Object to build a
orgsorgroupspage listing all the groups and orgs - A showcase page for a specific group or org
- You could even use some of our components e.g: You could get the datastore contents for a resource using the
ckan.datastoreSearch(resourceId: string)function and then display that as a line chart or vega chart.
CKAN API
Thanks to TypeScript, you can get a list of all the API methods in @portaljs/ckan and their respective input/output values from the autocomplete functionality on your own editor. Here is a list with all of them for quick retrieval:
getDatasetsList()- Gets a list of all the datasets in the portalgetDatasetsListWithDetails(options: DatasetListQueryOptions)- Gets a list of all the datasets including their respective resourcespackageSearch( options: PackageSearchOptions )- Callspackage_searchgetDatasetDetails(datasetName: string)- Callspackage_showgetDatasetDetails(datasetName: string)- Callspackage_activity_listand automatically fills in the user informationgetUser(userId: string)- Callsuser_showgetGroupList()- Gets all the groups in the backendgetGroupsWithDetails()- Gets all the groups in the backend with detailsgetGroupDetails(groupName: string)- Gets all the details from a single groupgetGroupActivityStream(groupName: string)- Get a group activity list and automatically fills in the user informationgetOrgList()- Gets all the orgs in the backendgetOrgsWithDetails(accrossPages?: boolean)- Callsorganization_list?all_fields=True. If you setaccrossPagestotrue, it will repeatedly call the API until all groups are returned.getOrgDetails(orgName: string)- Gets all the details from a single orggetOrgActivityStream(orgName: string)- Gets a org activity list and automatically fills in the user informationgetAllTags()- Gets all tags in system with detailsgetResourcesWithAliasList()- Gets all the resources in the datastore that have an alias assigned to themdatastoreSearch(resourceId: string)- Calls datastoreSearchgetResourceMetadata(resourceId: string)- Callsresource_showgetResourceMetadata(resourceId: string)- Callsdatastore_infoon a resourcegetFacetFields(field: string)- Gets the possible values eg: getFacetFields("tags") will get you all the tags that are currently assigned to a dataset + how many datasets have that particular tag.